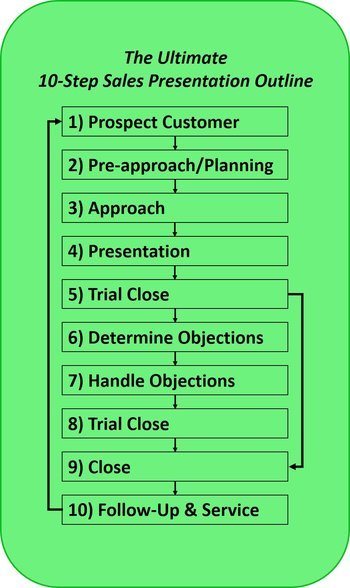
Pre-Approach Planning is Step 2 of your Ultimate 10-Step Sales Presentation.
First and foremost, Pre-Approach Planning is critical to your success as a salesperson. As a relational salesperson, you begin with a purpose and a plan. So, you must know what you plan to accomplish in the sales presentation and how it will be done. The most successful salespeople account for every variable and plan for every contingency.
Therefore, your Pre-Approach planning must be strategic!
That level of Pre-Approach Planning doesn’t happen by accident. The purpose of this article is to turn you into a Planning Ninja!
In this article on Pre-Approach Planning, we cover:
- What is strategic presentation planning?
- 4 reasons to plan your sales call.
- The 4 elements of your strategic plan.
- 5 elements of every sales objective.
- 6 things the customer profile should tell you.
- The 4-step customer benefits plan.
- Planning the presentation.
What is Strategic Presentation Planning?
A relational salesperson is in the business of solving problems. You learn about a customer’s problem, you find a way to solve their problem with your product, and you sell the customer your solution.
However, to succeed, you must be a strategic problem solver. That means you must be able to uncover the strategic needs of the customer, develop creative solutions, and arrive at mutually beneficial agreements.
Strategic Needs
The professional salesperson who understands the customer’s needs is in the best position to provide product solutions. For a salesperson to provide creative solutions to a customer’s problem, they must have an in-depth understanding of the customer and their needs.
Creative Solutions
Every customer is unique and has unique problems to solve. The professional salesperson can use creative problem solving to develop creative solutions that meet the customer’s needs.
Mutually Beneficial Agreements
A salesperson who understands the customer’s strategic needs and develops creative solutions is most likely to come to mutually beneficial agreements with their customer.
A problem-solving salesperson becomes a trusted consultant and ally in the customer’s business. This kind of mutually beneficial relationship is the basis of strong long-term relationships.
A relational salesperson who uncovers a customer’s strategic needs, and develops creative solutions to solve the customer’s problem, must then present the solution so that it establishes a mutually beneficial agreement. Salespeople who do this have a strategic customer relationship that will benefit both parties.
4 Reasons to Plan Your Sales Call
If you are a commission salesperson, you don’t make any money until you make a sale. If you are a salaried salesperson you won’t have your job very long unless you make a sale!
So, whether you are commission or salaried, you need to make sales. The best way to make a sale is to plan carefully every element of your sales presentation.
When successful salespeople are asked why they spend time planning their sales calls the answers they most often give are 1) increased confidence, 2) develops goodwill, 3) reflects professionalism, and 4) increases success.
1) Increased Confidence
I confess I am a nervous public speaker. Whether it’s a small group of executives or an audience of thousands, I get butterflies. But what I have always done to minimize anxiety and increase my confidence is to plan and practice. By planning every element of a presentation in advance, I know exactly what I want to say, in what order, and to whom.
2) Develops Goodwill
A salesperson who plans thoroughly by taking the needs of their customer into account and can better match their products with the customer’s needs. You build goodwill when you demonstrate your understanding of the problem the customer faces and how your product will solve their problem.
3) Reflects Professionalism
The adage, “prior planning prevents poor performance,” is as true today as when it was first uttered. A salesperson who plans thoroughly displays a level of professionalism, which is nonexistent in the salesperson who is a poor planner.
A professional buyer can spot a professional salesperson from a mile away. If you intend to be a professional salesperson, you must learn to plan effectively.
4) Increases Success
A salesperson who is well-prepared, confident, and professional will always outperform the unprepared salesperson. Which reminds me of another adage, “prior planning pays profits promptly.”
The 4 Elements of Your Strategic Plan
The strategic plan for your sales presentation includes four essential elements. These are 1) your sales objective, 2) the customer profile, 3) key customer benefits, and 4) the presentation itself.
1) Establish Your Sales Objective
Every sales presentation must be based on an established sales objective. Eager, young sales representatives often just want to meet the customer, see what develops, and sell what they can on the fly. Although we should certainly be flexible and ready to respond to unanticipated requests from a customer, this should be the exception, not the rule.
2) Develop Your Customer Profile
You need to know as much as possible about your customer and their business. The best way to understand a customer’s strategic needs, and for you to develop a creative solution to their problem, is to learn their business!
You must have a customer profile document for every customer. This document includes basic information about the customer and their business, how decisions are made, past purchase history, and personal information about key staff members.
3) Develop Key Customer Benefits
Customers buy benefits, not features. More than a few salespeople fall into the habit of selling the features of their product instead of what the product will do for the customer.
For example, “the fire truck is yellow” (feature). The “yellow fire truck can be seen from a greater distance” (advantage). The “yellow fire truck’s visibility reduces the possibility of an accident” (benefit).
Ask yourself, “what benefits does my product provide that will solve this customer’s specific problem?” These benefits are the key selling points, the backbone, of your presentation.
4) Develop the Sales Presentation
Finally! The step every salesperson has been waiting for; developing the presentation itself.
The presentation has several distinct phases. Based on all the information you’ve gathered about your customer; you develop your opening approach. After the opening, you’ll discuss your products benefits, your marketing plan, the business proposition, present a suggested order, and finally, close.
There is a lot to each of the four elements of your strategic plan so we will go into more detail on each of them, starting with how to develop a sales objective.
5 Elements of Every Sales Objective
Every sales presentation must be planned to achieve your sales objective. A good sales objective must have five elements. It must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. An easy way to remember the criteria for a sales objective is the acronym S.M.A.R.T.
Specific
Your objective must be specific. A specific objective answers the “who, what, why, where, when” questions. It is not good enough to say your objective is “to get an order,” or “sell a display of my product.” An order for what? A display of what?
Measurable
You won’t know if you achieved your objective unless your objective is measurable. Measurable objectives answer the “how much” and “how many” questions. For example, a more measurable objective is, “to sell Customer XYZ a 50-case display of 128-oz. Product X.”
Achievable
Your objective may be challenging but it still needs to be achievable. Therefore, given the availability of resources, knowledge and time is this objective reasonable? If not, you need to assess the barriers to success, and (if necessary), be prepared to revise your objective.
Relevant
Your objective needs to relate to you and your company. An objective that is relevant answers the “why” and “is this worthwhile” question. Ask yourself, is this objective in alignment with my personal objectives? Is this objective in alignment with my company’s objectives?
Time-Bound
Every objective must include a target date or a time limit. The objective that is time-bound answers the “by when” question. A target date establishes a sense of urgency and serves as a motivator to keep you focused on achieving your objective.
Now that you’ve established a SMART objective for your sales call let’s look at your customer profile and make sure you know everything that you need to know before making your presentation!
6 Things the Customer Profile Should Tell You
You should have a customer profile for every customer. Even simple businesses can benefit from having customer profiles. The hairstylist I used to go to (when I had hair) kept a card on every customer with basic personal information, how they liked their hair cut and styled, and products she used for each customer.
When I was leading selling teams who were responsible for making major presentations to executive groups, we developed customer profile binders of information. Those binders contained detailed information on all the key personnel, their business opportunities, major competitive issues, financial information, and more.
If you are selling to a large company where you have an ongoing relationship, you should have a customer profile that answers, at a minimum, these six questions.
1) Who Makes the Buying Decision?
Is the buying decision made by an individual or by a committee? If by a committee, who sits on the buying committee?
2) What is the Buyer’s Background?
Is the buyer new to this company or have they been there all their career? Does this buyer have a lot of buying experience, or are they new to buying? Is this buyer experienced with making buying decisions on this type of product? What does the buyer expect of you as the salesperson?
3) What Business Terms and Requirements Are There?
Does the customer have specific purchasing terms such as credit terms, or cash discounts? Do they have specific requirements for delivery, warehousing, or technical service? Do they have specific goals for return on investment for items they purchase?
4) Who Are the Key Competitors?
Who are your key competitors that are competing for this customer’s business? What services do they provide that differ from your own?
5) What are the Purchasing Policies?
Does this buyer only meet with salespeople on certain days or at certain times? Are their limits to the amount of time allowed for the presentation? Does this customer only purchase special promotions?
6) What is the Account’s History?
Do you have a purchasing history with this customer? What have they purchased in the past (from you or competitors)? Do they repurchase at regular intervals? Do they have slow periods where they stop purchasing altogether?
It is easy to see how you could fill a binder of information if you are dealing with a high-value sale to a large customer.
If you are inheriting information from a previous salesperson, you also need to make sure that you verify everything! Since conditions and requirements change frequently and without warning!
Now that we have our SMART sales objective and a complete customer profile let’s turn our attention to one of the most important aspects of the presentation; the benefit plan you will use to make the sale!
The 4-Step Customer Benefit Plan
The customer benefits plan is the core of your presentation. Your sale will almost certainly fail if you do not have a well thought out strategic benefit plan. After all, the goal of a relational salesperson is to sell a product that solves a customer’s problem. Your customer benefits plan is designed to help solve the customer’s problem so you can close the sale!
Developing a customer benefits plan is a four-step process that consists of
- identifying the right benefits to present,
- developing a creative marketing plan along with a
- solid business proposal so that you can close the sale with a
- suggested order!
Step 1: Select the Features, Advantages, and Benefits to Present
We touched on the subject of features, advantages, and benefits in the 4 Elements of Your Strategic Plan section. This is where most inexperienced salespeople struggle the most. It is easy to talk about product features all day long, but buyers buy benefits, not features.
If you want to stress the importance of a product feature to a buyer, you must describe the feature in terms of its advantage to the buyer and ultimately, the benefit that advantage provides.
Remember that a feature is a physical attribute like “the ambulance is white with red markings” or “the siren is 120-decibels.” An advantage is a performance characteristic. The advantage of a white ambulance with red markings is “it is recognizable and distinctive.” An advantage of a 120-decibel siren is “it can be heard from a great distance.”
The feature and advantage are helpful, but the real importance to the buyer is in the benefit they provide. The benefit results from the feature and advantage. The white ambulance with red markings “is easily recognized by people and has a calming effect on people in a stressful situation needing help.” The 120-decibel siren “increases safety for the driver and the public by reducing accidents.”
Most inexperienced salespeople try to list all the features, advantages, and benefits they can think of, but this is a mistake. Buyers want to hear the benefit that is most important to them first.
For instance, what problem are you trying to solve? A wise salesperson will discuss the feature, its advantage(s), the benefit that solves the buyer’s problem first! You can discuss other benefits, but only after you’ve discussed the benefit that solves the customer’s problem first.
Step 2: Develop Your Marketing Plan
If you are selling to a wholesaler or a retailer, you need a marketing plan. A smart real estate agent will develop a marketing plan to show a prospective home seller.
Your marketing plan should include suggestions for how the wholesaler or retailer can promote the resale of your product. In the wholesale channel, that might be special promotions, sales contents, product shows, etc. In the retail space, it might be special displays, advertising, shelf space, and pricing. In real estate, it might include placing the home in the multiple listing services, special photo layouts featured on home sites, staging the home, open houses, etc.
The goal of the marketing plan is to demonstrate how you can help the customer resell or use your product!
Step 3: Develop Your Business Proposition
The business proposition is often given little thought by some salespeople. Thus, for that reason, this is an area where many sales are lost. This is where we discuss the dry and seemingly boring details of how our business proposition works. We talk about things like price, cash discount terms, markup, return on investment, shelf space, and value analysis.
These are all the little details involved in the transaction between buyer and seller that make the business proposition a value proposition for the buyer! For some industries, these details are well known and fairly standard. A good example of industries where these elements are pretty standardized is retail clothing stores or grocery stores.
However, in some industries, like automobile sales, real estate, and construction, these details vary and are often subject to negotiation.
Step 4: Develop a Suggested Order
Finally! All our hard work comes together in the all-important salesperson, suggesting an order to the buyer. If the presentation has kept the customer needs in mind, the benefit plan will solve the buyer’s problem, the marketing plan gives the buyer confidence in their ability to resell the product, and all the details of the business plan are in order, then we are ready to ask for the order!
Planning the suggested order is usually not a difficult task, but it does require some thought. Therefore, it is an important part of the planning process. This suggested order considers things like the customer’s current inventory, the customer’s turnover rate, what should be bought, the suggested quantity, the assortment, and when it will be delivered.
Although, we’ve done a lot of work to get to this point in our planning process. There is still one key planning step that remains, which is pulling all this information together into a powerful, persuasive presentation!
Planning the Presentation
Our strategic presentation planning process is nearly complete. We have only one final thing to plan, and that is how we will bring all this information we have gathered together and presented it to our buyer in a concise, powerful, and persuasive manner.
Organizing all this information and presenting it in a logical flow is critical. A logical flow has the benefit of helping you as the salesperson to stay on track, and it will make it easier for the buyer to understand you.
Six Major Phases of Your Presentation
Your presentation includes six major phases; the approach, a discussion of your product, your marketing plan, your business proposition, the suggested order, and the all-important close.
1) Approach
The purpose of the approach is threefold. You need to build rapport, uncover/confirm needs, and gain the buyer’s interest in your solution as you transition into the presentation.
2) Fully Discuss Your Product
When you are discussing your product, your focus should be on the features, advantages, and benefits of your product that will solve the buyer’s problem. Remember to select the feature, advantage, benefit combination that is most important to the buyer and present it first. Then, and only then, should you discuss additional details about your product.
3) Present Your Marketing Plan
If you are selling to a retailer or wholesaler, your marketing plan is all about how to resell your product. If you are selling to a consumer or an industrial buyer your marketing plan is all about how to use the product.
4) Explain Your Business Proposition
Don’t overlook the importance of the business proposition. Plan out how you will discuss all the important details of the transaction that are most important to this buyer.
5) Suggest Purchase
Your suggested order should meet the needs of the buyer. It should consider their current and forecasted situation.
6) Close
Finally, close. Ask for the order. A surprising number of salespeople do all the work of getting this far in their presentation and then fail to close. So, you need to plan your close with great care, just like all the rest of your presentation.
BONUS: The Prospect’s Mental Steps
As you are delivering your presentation, the buyer is receiving the information you deliver and thinking about how what you said will solve his problem.
As a salesperson, you need to move the buyer’ mental process along on a continuum from gaining his/her attention to being interested in what you have, to have a desire for the product, and to be convinced it is the right product before they are ready to make a purchase. This process is known as the buyer’s mental steps to purchasing.
Attention
From the moment you say “hello” you need to capture and maintain the buyer’s attention. As soon as you have the buyer’s attention, move quickly to secure the buyer’s interest.
Interest
If you’ve done all your pre-approach planning, you will then have a pretty good idea of what is most important to the buyer. So, you need to confirm what is important with the buyer and then quickly link your product to the buyer’s needs. If the buyer is leaning forward, listening to you and engaging in the conversation, you know they are interested in the presentation.
Desire
Your buyer is interested in learning more about how your product can solve their problem. It’s time to elevate their interest to the desire by demonstrating how the feature, advantage, benefit of your product will solve their problem. When you do this, the buyer will express desire for your product as being a way to solve their problem.
Conviction
Even though the buyer may have a desire for your product, they may not yet be convinced it is the best solution for them. Focusing on how your product solves their problem, the marketing plan, and the business proposition will convince the buyer that your product is the right choice!
Purchase
Once the buyer has reached the conviction stage, they are ready to take action or to purchase. Make the decision to purchase simple with an easy next step, and then close the sale!
Congratulations! You have successfully completed a strategic presentation plan! I’m sure you realize every selling situation and every buyer is different and will require a different approach to planning. But make no mistake, a professional salesperson makes a plan and sells the plan!
The Ultimate 10-Step Sales Presentation Series
Step2: Pre-Approach Planning is the third in a series of articles, which have been created to teach you how to craft and deliver the Ultimate Sales Presentation in 10-Steps.
If you missed a prior article in this series or you want to review one again, you’ll find them here:
Kick-Off: The Ultimate 10-Step Sales Presentation
Step 2: Pre-Approach Planning (you’re here)
Steps 3-10: Coming soon. A new article releases every two weeks.
If you want to make sure you don’t miss one of these articles you can sign up to receive the series here.
Join the Conversation
As always, questions and comments are welcome. What questions do you have about the Pre-Approach Planning step of the Ultimate 10-Step Sales Presentation model?
I’d love your help. This blog is read primarily because of the people like you who share it with friends. Would you be kind enough to share it by pressing the share button?
Category: Salespeople












